
Sign Up and Get 10% Extra Discount

An evidence-based review of a promising intervention.
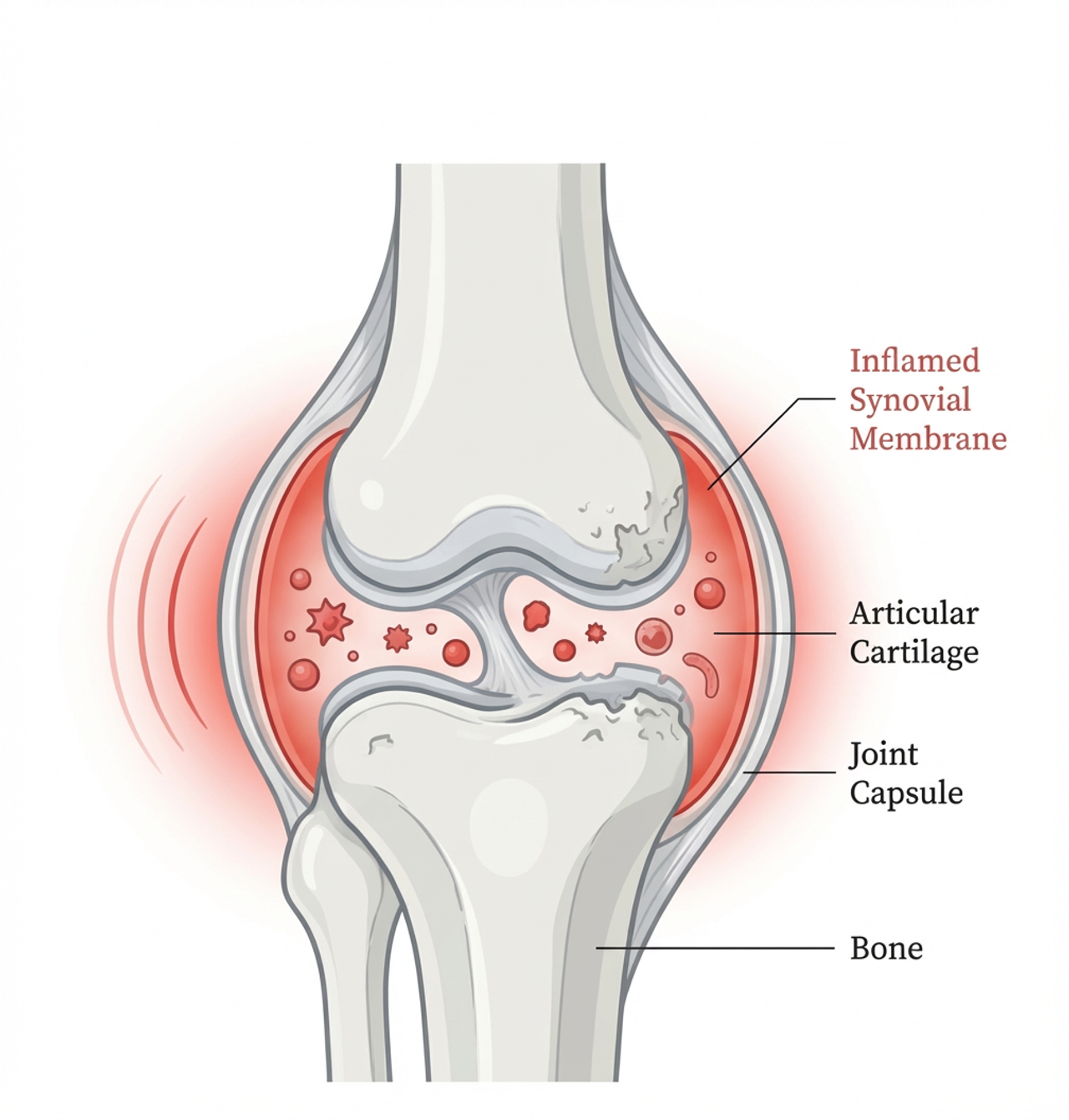
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disorder characterized by persistent systemic inflammation. For patients, this translates into a daily reality of:
A clinical trial was conducted to evaluate the efficacy of Vitamin E as a therapeutic agent for RA.

Patients receiving Vitamin E experienced dramatic improvements in the primary physical symptoms of RA.
 76%
Improvement
In tender joints
76%
Improvement
In tender joints
 62%
Improvement
In painful joints
62%
Improvement
In painful joints
 61%
Improvement
In swollen joints
61%
Improvement
In swollen joints
The physical improvements were mirrored by a significant reduction in key blood markers for systemic inflammation.

In C-Reactive Protein (CRP), a primary marker for acute inflammation.

In Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR), indicating a decrease in chronic inflammation.
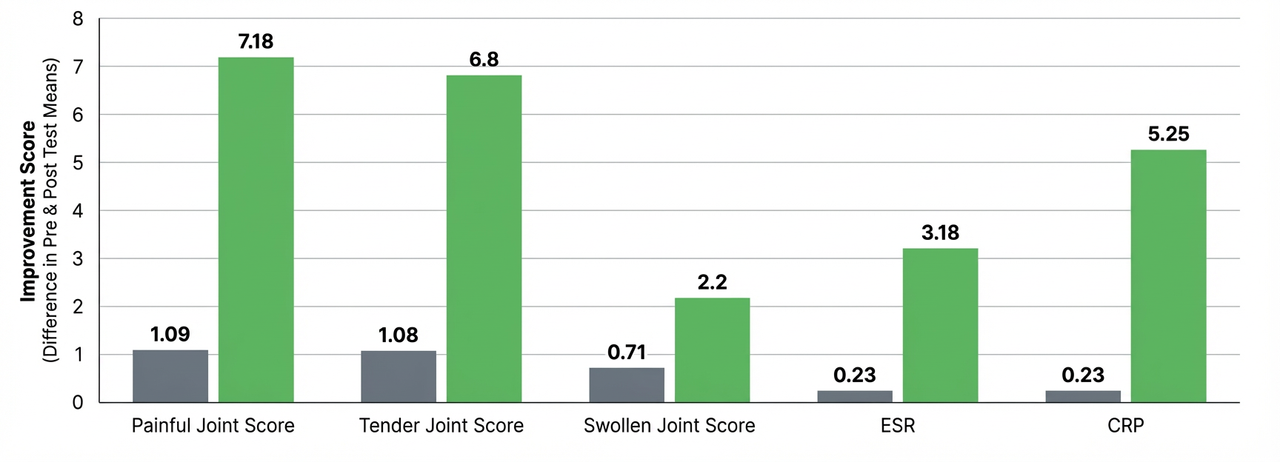
A direct comparison of the improvement scores between the Vitamin E and control groups reveals the intervention’s overwhelming efficacy. The chart shows the mean difference in scores before and after the test period.
The clinical results are underpinned by Vitamin E’s multifaceted biological activity. Its efficacy stems from three primary pathways that directly counteract the pathology of Rheumatoid Arthritis.
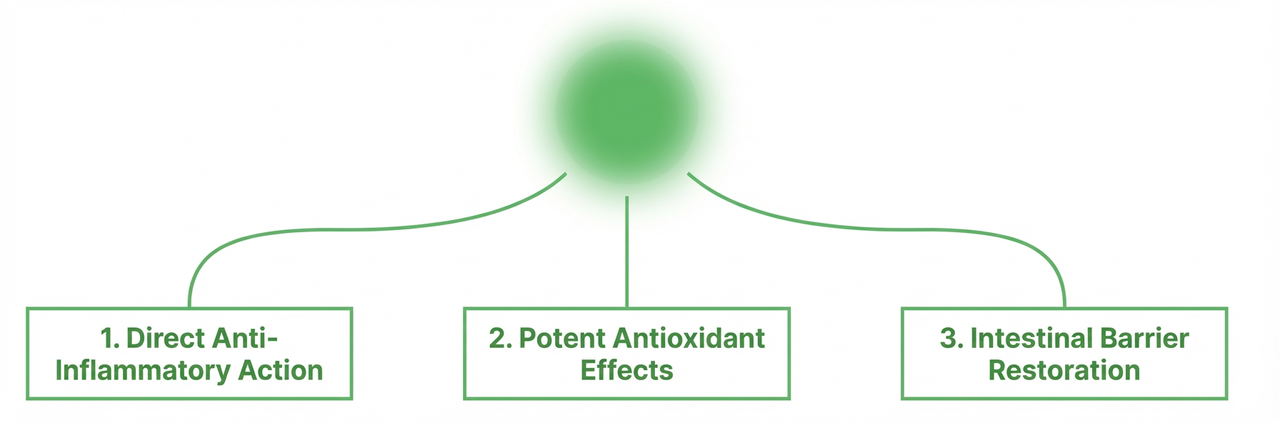

The evidence demonstrates that 400 mg of daily Vitamin E:
These findings position Vitamin E as a significant, evidence-backed complementary therapy in the holistic management of Rheumatoid Arthritis.

Premium, Natural Solutions for Your Health



